Project 2025, the Heritage Foundation’s blueprint for a second Donald Trump presidency—you know, that document he knows nothing about even though 140 people from his first administration, including six former Cabinet members, helped create it—is full of delightful little Easter eggs. One provision that has attracted almost no public notice, perhaps because it seems so reasonable, is the authors’ call for the government to create “universal savings accounts” (USAs).
Heck, it even has a patriotic name!
All taxpayers should be allowed to contribute up to $15,000 (adjusted for inflation) of post-tax earnings into Universal Savings Accounts (USAs). The tax treatment of these accounts would be comparable to Roth IRAs. USAs should be highly flexible to allow Americans to save and invest as they see fit, including, for example, investments in a closely held business. Gains from investments in USAs would be non-taxable and could be withdrawn at any
time for any purpose. This would allow the vast majority of American families to save and invest without facing a punitive double layer of taxation.
But let’s think about this. Over the past few decades, Congress passed a series of bills to help Americans save for old age privately via government-subsidized pensions, 401(k)-type plans, and individual retirement accounts—of which Roth IRAs are one type. These tax breaks and program expansions have all been bipartisan, and all have passed with flying colors, because they sound pretty good—much like these universal savings accounts—until you examine them more closely.
And then you have to ask: Good for whom?
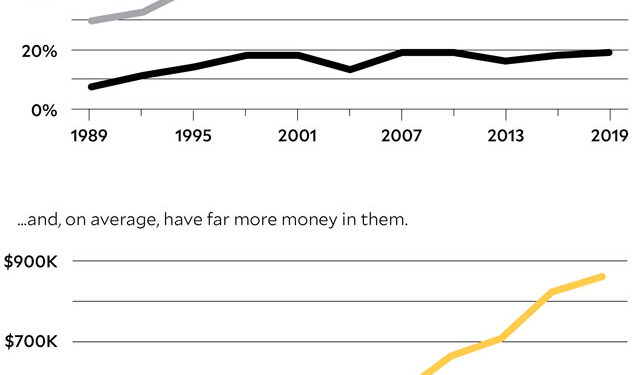
Taken collectively, the various retirement subsidies are mind-bogglingly expensive. They are, in fact, the federal government’s single largest tax expenditure, projected to deprive the Treasury of almost $2.5 trillion over five years (2023–2027), according to the bipartisan Joint Committee on Taxation (JCT)—mostly, as I’ve written, to the wildly disproportionate benefit of our most affluent.

In the most extreme case reported thus far (by ProPublica), the Silicon Valley entrepreneur and political puppet-master Peter Thiel used a $1,700 contribution to his Roth IRA—Roths are intended for middle-class savers—decades ago to purchase 1.7 million “founder’s shares” of PayPal at one-tenth of a cent each. Because of that, by 2002, the year eBay purchased PayPal, ProPublica reported, the balance in Thiel’s Roth was up to $28.5 million, with all of those gains nontaxable. He then repeated this cycle with other fledgling companies, culminating in a Roth IRA containing north of $5 billion in assets.
Thiel was an outlier, but ProPublica identified others with IRAs worth tens or hundreds of millions of dollars. Indeed, in 2021, at the request of Senate Finance Committee chair Ron Wyden (D-Ore.), the JCT counted more than 28,000 taxpayers with traditional or Roth IRAs with balances exceeding $5 million—497 of the accounts contained $25 million or more.
What does this have to do with Project 2025? Well, USAs would be Roths on steroids. The $15,000 annual contribution limit is more than twice what people under 50 are allowed to contribute to a Roth. And even the highest earners could contribute to a USA—with Roths, you can only make the full contribution if your income is $146,000 or less. The fact that one needn’t wait until retirement to withdraw funds make USAs all the more compelling.
Heck, if you can afford to put $15,000 a year into an investment fund and let it take a tax-free ride—which the majority of Americans cannot—there would be no reason not to. “High bracket taxpayers would get the biggest tax benefits and could find the disposable savings to participate most easily,” says Steven Rosenthal, a senior fellow at the Tax Policy Center who has written about the retirement system’s income and race disparities.
Roth IRAs cost taxpayers relatively little, mainly because most people play by the rules. USAs would obliterate the rules, and cost the government a pretty penny.
But the real poison pill is this line: USAs should be highly flexible to allow Americans to save and invest as they see fit, including, for example, investments in a closely held business.
That sounds an awful lot like what Thiel did. Or, for example, a private equity fund manager could put his “carried interest” in a USA at the outset of a project. A CEO could contribute tens of thousands of shares of cheaply acquired stock options before the company goes public. A garage inventor—like Bill Gates once was—could value his company initially at $15,000 and put all of the stock into his USA. It’s not worth much now, but wait 10 years—Jackpot!
“Their tax avoidance potential would be infinitely greater. They would have the potential to exempt multibillion-dollar gains, even trillion-dollar gains, from taxation,” tax attorney Bob Lord and Morris Pearl, chair of Patriotic Millionaires, wrote in a Fortune commentary.
“Allowing taxpayers to invest ‘as they see fit,’ could fuel stuffing…when an individual uses a tax-free account to acquire non-publicly traded assets at prices below fair market value,” Rosenthal told me in an email. (He and New York University law professor Daniel Hemel have written to the Senate Finance Committee, urging lawmakers to crack down on the practice.)
Whether Thiel’s Roth magic trick violates current IRS rules on “prohibited transactions” is a private matter for him and agency lawyers to hash out—but legal minds who have thought it through see some potential red flags. What’s more, the IRS has issued guidance that deems similar-sounding strategies “abusive” and says it views them as “tax avoidance transactions.”
Democratic presidential nominee Kamala Harris regularly asks Americans to imagine Donald Trump without guardrails. Well, imagine Roths without guardrails—larger contributions, no income cap, and no rules about how the funds can be invested. Roth IRAs in particular cost US taxpayers relatively little—about $14 billion a year—mainly because most people play by the rules. USAs would obliterate the rules, and in doing so, cost the government a pretty penny.
But this isn’t just about tax revenues. The bigger problem is how wildly inequitable America’s wealth and income distributions have become over the past four decades, a shift that started with the wealth-friendly tax cuts of the Reagan era. In a new report, the Congressional Budget Office notes that the average 2021 household income for the top-earning 1 percent of taxpayers was $3.1 million—42 times the household average for the bottom 90 percent. That’s the most lopsided income distribution on record since the government began tracking the data in 1979. Back then, the income disparity was 12 to 1.
America has ceased to be recognizable as a land of opportunity—or rather, one must now ask, a land of opportunity for whom?
USAs would be worth considering if Congress limited them to people with few assets who earn less than $100,000, for example, and imposed strict rules to prevent wealthy investors from gaming them for tax avoidance. As proposed by that nonprofit Trump knows nothing about, they would make our class divisions even worse. And that would truly be unaffordable.