One August evening, I drove through the cornfields and dairy farms of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, to attend a government-themed prayer night at Ephrata Community Church. The sprawling house of worship looks like an office park and houses a cafe and an indoor playground in addition to a large sanctuary. This event, however, was in a converted barn across the parking lot called Gateway House of Prayer. For the last 15 years, it has been open 24 hours a day for the faithful to worship when the main church is closed, with parishioners keeping watch in shifts.
It was a Thursday night. Gradually, about 22 congregants, mostly seniors, all of whom were members of the community, filtered in. Over the next two hours, the group prayed, sometimes quietly and sometimes very loudly, and sometimes in strings of syllables, a charismatic Christian tradition known as speaking in tongues. Of the prayers that I could understand, many were what you’d hear in any church—gratitude for God’s goodness or entreaties for family members going through hard times.

But interspersed were more unsettling messages: frequent references to the “enemy,” to a battle between good and evil, to a “spiritual war” playing out in our country. One prayer leader encouraged attendees to join a pair of “prophets” who were taking daily Communion for 90 days at exactly 4:14 p.m. Why so precise? The answer can be found in two Old Testament verses: Esther 4:14, which says Christians are called to speak up in the face of persecution, and Nehemiah 4:14, which “is about fighting,” the prayer leader said, “on behalf of our sons, our daughters, our families.”
The devotees she mentioned were leaders in the New Apostolic Reformation, a charismatic evangelical Christian movement led by a loose network of self-appointed prophets and apostles, who claim that God speaks directly to them, often in dreams. They believe that Christians are called to wage a spiritual battle for control of the United States. In the vanguard of an ascendant Christian nationalist movement, they are seeking an explicitly Christian command of public schools, social policy, and all levels of the government, including the courts. Some scholars claim NAR is the fastest-growing spiritual movement in the United States. Evangelical writer C. Peter Wagner described it as the most significant shake-up in Protestantism since the Reformation. Its laser focus on starting a spiritual war to Christianize America has led the Southern Poverty Law Center to call NAR “the greatest threat to US democracy that you have never heard of.”
“It’s the transformation of an entire society…something so transcendentally revolutionary that most people never even thought about something like this.”
Estimates of Christians influenced by NAR vary widely, from 3 million to 33 million. But the number of adherents isn’t the extent of its influence; its main tenets have moved beyond the confines of churches and into the political mainstream, largely thanks to traveling apostles and prophets who preach at evangelical churches all over the world. Fred Clarkson, a senior research analyst with the extremism watchdog group Political Research Associates, described the New Apostolic Reformation as a seismic cultural shift. “It’s the transformation of an entire society with this certain kind of Christo-centric worldview,” he told me. “We’re talking about something so transcendentally revolutionary that most people never even thought about something like this.”
Donald Trump’s former national security adviser Mike Flynn has hosted NAR leaders on his “ReAwaken America” tour, and House Speaker Mike Johnson (R-La.) has worked with its apostles. Just this past weekend, GOP vice presidential hopeful Sen. JD Vance (R-Ohio) appeared in Pennsylvania at an event hosted by Lance Wallnau, a Texas business strategist-turned-NAR superstar. Wallnau, who has called Kamala Harris a “Jezebel” and speculated that people on the political left may be controlled by demons, helped develop Project 19, a right-wing political initiative to win 19 key counties in swing states for Trump.
I asked Clarkson for a metaphor to describe how New Apostolic Reformation concepts have spread beyond the confines of the movement. At first, he suggested the cellular process of osmosis, or perhaps a tea infusion, but neither accounts for the intentionality of the movement’s leaders. “How do you infuse your Christian ideas into Babylon?” he asked, referring to an ancient city that rejected God. “That’s the nature of their thinking. It can be deeply subversive. It can also be utterly in your face.”
Since 2016, many NAR prophesies have concerned Trump, whom adherents see as having been divinely chosen to lead the country. Trump’s introduction to the movement came in 2002 when he invited Florida apostle Paula White-Cain to be his personal minister after seeing her preach on television. By the time he became president, he had acquired a handful of other NAR spiritual advisers: most notably, a South Carolina–based apostle named Dutch Sheets and prophet Cindy Jacobs, who helms an influential ministry in Texas. Throughout his presidency, Trump’s NAR counselors were mostly ignored by White House reporters, dismissed as latter-day versions of evangelical pastor Billy Graham with Richard Nixon, or Jeremiah Wright with Barack Obama. Yet “these are the key religious people around Donald Trump and the people who brought him the presidency,” Clarkson said. “They’re the people who influenced his presidency and the people who are leading the religious wing of his reelection campaign.”
As the 2020 election drew near, their role became more important. White-Cain warned her followers that Christians who don’t support Trump will “have to stand accountable before God one day.” Shortly after Trump’s defeat, Sheets became an influential figure in the “Stop the Steal” campaign, leading rallies across the country. He warned that the results of the presidential election were “going to be overturned and President Trump is going to be put back in office for four years.” Around the same time, White-Cain gave a speech imploring religious Americans to “strike and strike and strike and strike and strike and strike and strike and strike and strike and strike until you have victory.”
Eight days before the Capitol insurrection of January 6, 2021, a group of apostles held a strategy meeting with Trump and his advisers. In a January 1 blog post, Sheets shared a dream from a prophet named Gina Gholston, in which she described “moving toward the Capitol, not at a full gallop, but at a steady, determined, fast trot. As we began, written in white letters on the ground in front of us were the words, ‘DON’T STOP.’” A year after the insurrection, Sheets recounted a dream in which Trump had told him that he would be a “political martyr” because, he had said, loosely quoting the Bible, “‘God has put the tools in me to tear down, root up, and confront the system.’”
NAR leaders have targeted the Supreme Court, too. In 2018, during Justice Brett Kavanaugh’s contentious confirmation hearings, Sheets urged his followers to ask God to grant them “a majority of Justices who are Constitutionalists, literalists (meaning they believe the Constitution is to be taken literally, exactly as it is written), and who are pro-life.” He prayed for “another vacancy on the Court soon,” which he felt was “coming quickly.” In a broadcast, Wallnau, the NAR leader who recently hosted Vance in Pennsylvania, described the accusations of rape against Kavanaugh as a spiritual attack.
The apostles’ visions for the Supreme Court didn’t get much mainstream attention—until the New York Times broke a series of stories about flags displayed at the homes of Justice Samuel Alito. Outside his main residence was an upside-down American flag, a symbol associated with the effort to overturn the 2020 presidential election. At his vacation home in New Jersey, the Times’ Jodi Kantor later reported, flew an “Appeal to Heaven” flag—belonging to Alito’s wife, Martha-Ann—showing a lone pine tree, a Revolutionary War symbol that had been revived and popularized by none other than Sheets. Rolling Stone found the same flag fluttering outside the Maine vacation home of Leonard Leo, the deep-pocketed conservative judicial kingmaker whose largesse has extended to several justices and their families.

Meanwhile, NAR apostles have ensured that their teachings have spread into local civil societies. In Redding, California, the 11,000-member Bethel Church now funds the local police force and trains public school teachers. In Pasadena, Korean American apostle Ché Ahn’s Harvest Rock Church bankrolled local candidates, including one for state Senate. The Remnant Alliance, an NAR-affiliated group, teaches Christians across the nation to run for school boards.
And then there is Lancaster, Pennsylvania, a county of 550,000 people spread out over a patchwork of fertile farmland, where I traveled to understand what this kind of local transformation looks like. Since the mid-1600s, Pennsylvania has been known for religious fervor. First came the Quakers, followed shortly after by the Anabaptists, or “plain” people. Ephrata, for example, was a hub for the Brethren, but the area is also known for Mennonites and particularly the Amish. Today, Lancaster also has become an NAR hub. A popular sports event venue hosts far-right Christian conferences. NAR-affiliated churches control the school boards. One local group holds Bible study in public schools; another baptizes students in portable troughs in front of public high schools.
At the prayer night I attended, spiritual warfare rhetoric was on full display. An elderly woman described Lancaster public schools as being “so infiltrated with evil,” she prayed that “school boards would open up their eyes and ears and stop just screaming things that they think are good. If they did their homework, they’d see they’re not good.” Another woman announced that she had a vision of a claw machine. Instead of cheap prizes at the arcade, her claw—which symbolized the demonic influence of secularism—had picked up people’s minds so that they “can’t discern what’s right and wrong.” Her metaphor became an entreaty to God: “And I want to say…drop those minds and take them back for the Lord.” Someone blew a shofar, the ram’s horn that ancient Israelites used to call their armies to battle.
“We declare that this gender confusion would be stopped in the mighty name of Jesus!”
“We declare that this gender confusion would be stopped in the mighty name of Jesus!” cried another man, clad in the iconic Trump campaign T-shirt bearing the mugshot of the former president emblazoned with the word “wanted”—not for a crime but for another term in office. “We say, ‘Fight, fight, fight, hallelujah!’” he said. “We take the example of Donald Trump!” The group broke out in a chorus of “Fight, fight, fight!”

The New Apostolic Reformation may be influential, but it’s also hard to pin down. With no single leader, annual conference, or website outlining statements of belief, it isn’t a distinct Protestant denomination, like Baptists or Presbyterians, but a vast and amorphous network of prophets and apostles who oversee their own ministries, issue prophetic declarations, and journey to churches all over the world to spread their ideology. Though many adherents fit the stereotype of the white, male Christian nationalist, some of the most prominent American apostles are African Americans and women; some of the most powerful global apostles come from African nations. But in Lancaster, the churches are overwhelmingly white.
The term “New Apostolic Reformation” was coined in the 1990s by the influential evangelical writer Wagner, who emphasized that he was not the movement’s leader—because it had none. It was instead a coming together of several smaller sects that shared a belief that God appointed apostles and prophets who possessed special “gifts of the spirit,” like the ability to perform miracles, for instance, or speak in tongues. In what became known as the “fivefold ministry,” NAR churches organized themselves into five areas of leadership: apostles, prophets, evangelists, pastors, and teachers. Leaders were urged to “use their influence to create an environment in which the blessings and prosperity of the Kingdom of God can permeate all areas of society,” to conquer “the Seven Mountains: Religion, Family, Education, Government, Media, Arts & Entertainment, and Business.”
It was Wallnau who popularized this doctrine of Christian dominion, which is sometimes known as the Seven Mountain Mandate, or 7MM. According to a recent Denison University poll, between March 2023 and January 2024, the percentage of Christian Americans who believed in the Seven Mountain Mandate increased from just under 30 percent to 41 percent. The concept routinely appears in conservative political discourse. Alabama Chief Justice Tom Parker, who championed fetal personhood in a February 2024 ruling, said in an interview with a prominent NAR apostle that “God created government” and “that’s why he is calling and equipping people to step back into these mountains.”
Promoting a Christian nation has seeped into some of the Supreme Court justices’ opinions. In the 2019 case American Legion v. American Humanist Association, the court ruled in favor of the American Legion, which had erected a 40-foot cross on public land in Maryland. Alito wrote that taking down the cross would be “aggressively hostile to religion.” In the 2022 Kennedy v. Bremerton School District case, the court ruled 6–3 in favor of a public high school football coach who lost his job for routinely leading prayers during games. Writing for the conservative majority, Justice Neil Gorsuch unilaterally declared that the court had “long ago abandoned” a decades-old precedent that established that government employees can’t advance a particular religious ideology.
After the court declined in February to take up a case filed on behalf of people who had been removed from a jury because of their belief that gay marriage was wrong, Alito wrote in an unusual personal statement that he worried “Americans who do not hide their adherence to traditional religious beliefs about homosexual conduct will be ‘labeled as bigots and treated as such’ by the government.”
“There’s very little question that [Christian nationalist] views are very much reflected in where this Supreme Court majority is on religion and church and state.”
The perception that Christians are being persecuted by the government is a potent rallying cry of the Christian nationalist movement. Elliot Mincberg, a Supreme Court scholar and fellow with the pro-democracy organization People for the American Way, said, “There’s very little question that [Christian nationalist] views are very much reflected in where this Supreme Court majority is on religion and church and state.”
Clarkson has watched as the ideas popularized by NAR—the Seven Mountain Mandate, the fivefold ministry, and the concept of spiritual warfare—have infiltrated churches that aren’t officially connected to the movement. “There are so many Christianities, and they change over time—this is a perfect example,” he said. “People don’t necessarily know where every belief they hold came from.”
NAR also appropriates Jewish imagery. Two days after I heard one shofar at Ephrata, I attended an all-day “prayer burn” at a barn in the countryside where several attendees blew them. Others wore tallitot, or Jewish prayer shawls. A group of tween dancers carried a chuppah, a four-posted canopy often used in Jewish weddings. The group sang in Hebrew as they danced the hora, a standard feature in Jewish celebrations. Then, one of the NAR leaders I recognized from Ephrata took the microphone and began to speak about Jesus. “He’s the Lord of hosts,” she said. A cacophonous roar of shofars came from the crowd.
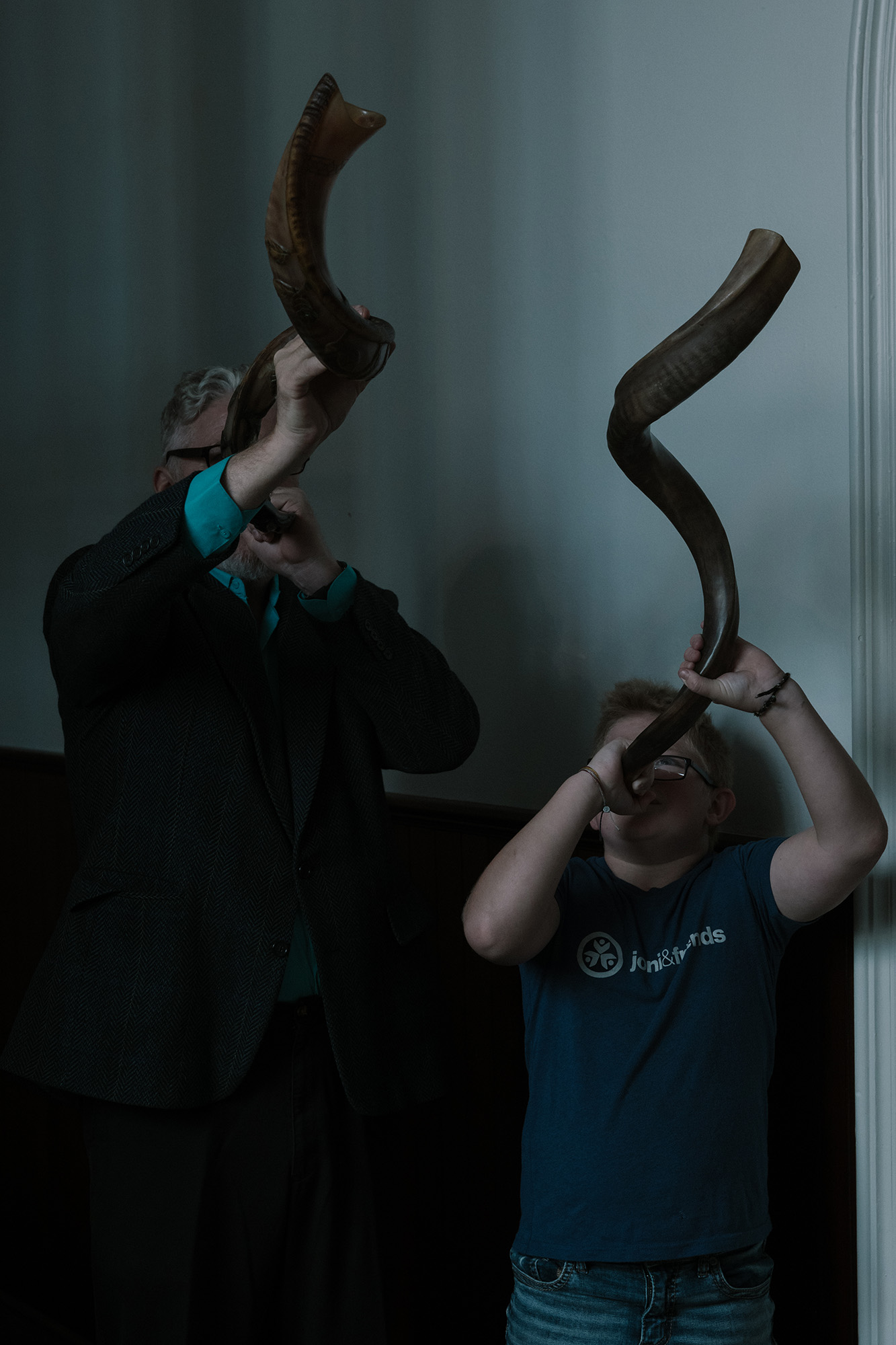


When I asked an attendee about all the Jewish references, she explained that it was simply a way to acknowledge the shared heritage between Christians and Jews. But that’s not the whole story, as Clarkson later reminded me. Many NAR adherents believe “that they have a special role as Christians in the end-times to deliver Israel”—a time when Jews will finally recognize Jesus as their Savior.
Lancaster has been home for centuries to the plain people, the Amish, the Mennonites, and the Brethren who, to various degrees, eschew machines and other trappings of modernity. But its demographics have shifted markedly over the last few decades. About 7 percent of Lancaster’s senior citizens are people of color, compared with a quarter of the youth. The gap between registered Democrats and Republicans has also narrowed.
Much of this purpling is taking place in the cobblestone streets and stately brick buildings of Lancaster City, which has welcomed 5,000 refugees to its population of 58,000 over the last 20 years. When I visited, I encountered a street festival in full swing. Young people grabbed overflowing plates of chicken tikka from an Indian food truck, and a crowd around the main stage danced to the music of a Liberian hip-hop artist.
“The way that you’re going to heal society is that you’re going to eliminate many government functions.”
City officials may embrace this diversity, but county leaders don’t. In February, the Lancaster City Council passed a law prohibiting police and city employees from asking people about their immigration status; county commissioners promptly declared Lancaster a “non-sanctuary” county. In June, after the City Council passed a resolution calling for a ceasefire in Gaza, County Commissioner Josh Parsons called the move a “propaganda victory for Hamas.” Lancaster’s overwhelmingly Republican state representatives tend to side with the county, even publicly denouncing the city’s efforts to welcome immigrants.
These state representatives regularly interact with NAR leaders. In May, two of them met with Sean Feucht, an NAR-aligned pastor who travels the country holding prayer rallies on the steps of state Capitol buildings. Also present at the meeting was a local self-proclaimed prophet named Abby Abildness, who works with the state’s prayer caucus group inside the Capitol to promote Christian initiatives in government. She has spoken candidly about her desire to blur the boundaries between church and state. “We need them and they need us,” she said, “because we can’t go write those laws.”
NAR influence in Lancaster churches began appearing in the early 2000s, but the Covid culture wars accelerated its spread. Six years ago, when Rebecca Branle, the owner of a local bike shop and mother of three, moved to Ephrata, she knew her family might stand out because they didn’t attend church. “We weren’t religious like everyone else, but I didn’t think it was that big of a deal,” she recalls. But in 2020, the pandemic hit, and once-negligible differences became “flash points.” After Branle posted a rainbow flag and a Black Lives Matter sign on her property, someone shot a bullet through the barn window, and in another incident, someone left a single slab of granite outside; “Look Behind You” was written on it in permanent marker, accompanied by a smiley face with the eyes crossed out. In smaller print appeared “Gays will burn in hell” and “You can repent.” She was scared for her family’s safety, but also confused: “Especially this community of people who say they’re so religious, suddenly this kind of talk is okay with them?”
The pandemic frightened many evangelical church leaders as well, but not because of the illness. Closing churches and mask mandates, which some considered offensive to God, were the real concern. Some pastors called vaccines the “mark of the beast.” To them, the pandemic’s major lesson was that government had become too powerful—and Christians had neglected to exert influence over that mountain.
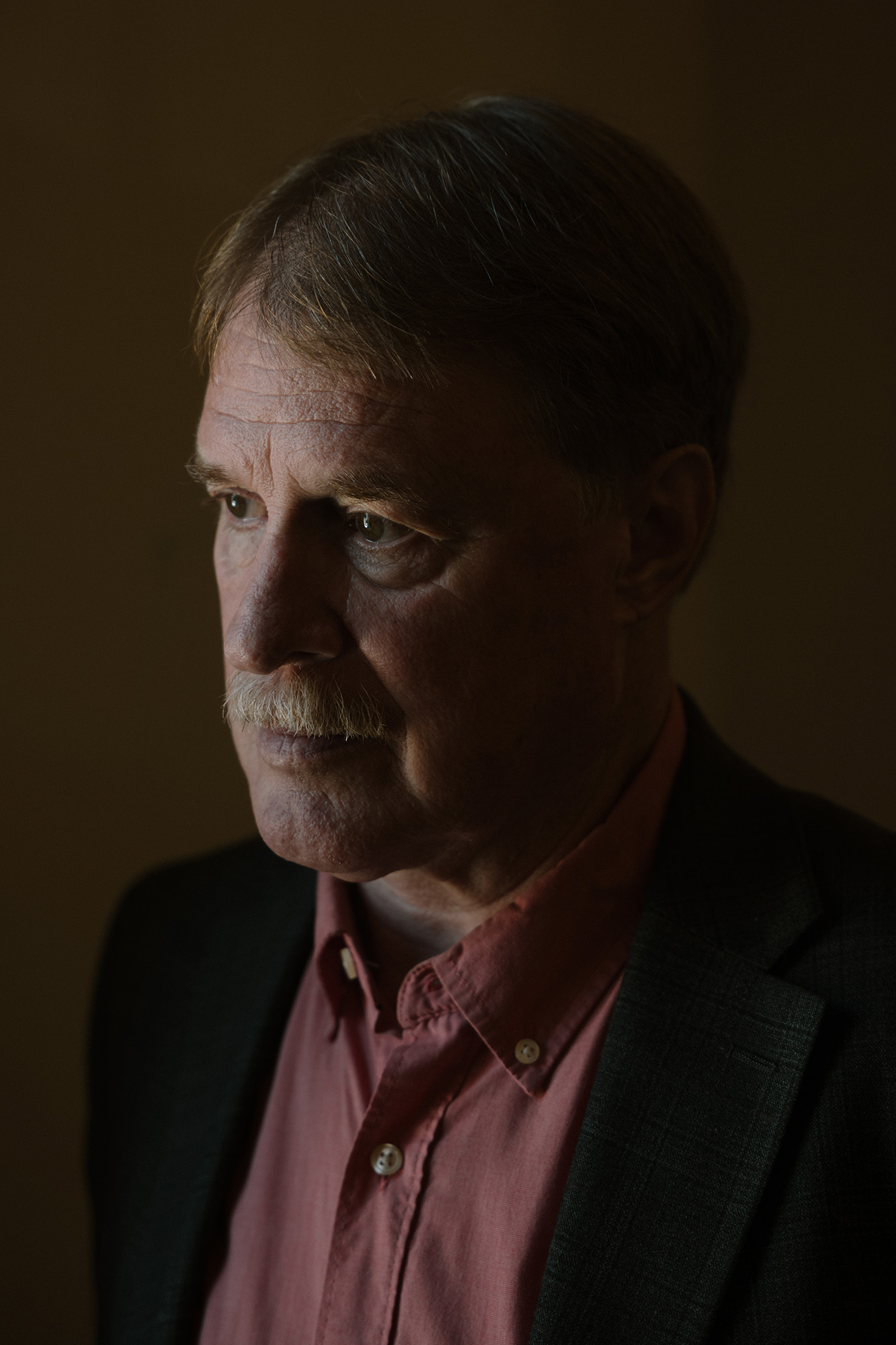

Don Lamb, an ebullient, redheaded pastor whose complexion turns ruddier when he gets excited, felt the impact of Covid profoundly. We sat in the basement of LifeGate church in the small Lancaster enclave of Elizabethtown, population 12,000, and Lamb described how once his congregation of 150 “were just doing our things, staying within our four walls, preaching the gospel.” But when mask mandates came into effect, “it was authoritarian into the nth degree, and so that awoke the church to say, ‘We need to be involved here.’” In sermons, Lamb and his brother and co-pastor, Doug, urged their congregation to oppose not only pandemic restrictions but also mail-in ballots, critical race theory, “pronoun protocols,” and other culture war issues. When Joe Biden won the 2020 election, the Lambs believed that his victory was the result of coordinated election interference by the left.
“Who gets to define the vision of society—only the liberals and secularists? That’s what makes us more determined to fight.”
On January 6, 2021, Don Lamb and several parishioners went to the rally outside the US Capitol. What was meant to be a peaceful gathering, he said, became violent only after police “were already throwing or launching flash-bang grenades at the audience.” He believes that the protesters who breached the building were set up and that the chaos could have been avoided. “We could have surrounded the Capitol with 100,000 Christians arm to arm just saying, ‘Grace, Amazing Grace,’” he said, “and there would have been no protesters who would have broken that line.”
Lamb follows Lance Wallnau, and he subscribes to the Seven Mountain Mandate. Trump, he told me, “was providentially given the stage of America.” Yet he doesn’t consider his church to be part of NAR. The term “Christian nationalism” irks him. The real problem with our nation, he says, is “liberal nationalism’s” obsession with cancel culture, identity politics, and elite institutions. “Who gets to define the vision of society—only the liberals and secularists?” he asked me. “That’s what makes us more determined to fight.”
Don and Doug Lamb often refer to the persecution of Christians in their sermons. The previous Sunday, Doug began by urging his congregation to love their neighbors, even those with whom they disagreed. But by hour’s end, he was berating Muslim immigrants in England who have “taken over the entire country” instead of assimilating. When a Muslim visits, he said, “They’re not coming as a guest. They want to take over your house.” He likened this to the futility of seeking peace with those who follow Satan—like gay people who “destroyed the church in America,” he said. “You can’t compromise the truth and have peace with people who are diabolically opposed to what you believe.” Later, Lamb clarified that a better way to phrase this sentiment might have been: “You shouldn’t compromise the truth to be at peace with those who oppose you.”

Some LifeGate congregants appear to be using those messages to inform local politics. In 2021, three church members won seats on the Elizabethtown school board, flipping it to a conservative majority. This past June, the school board voted to work with the Independence Law Center, a Christian law firm that has worked with school boards to ban transgender athletes in the county. A tertiary branch of the Family Research Council—a group that has long advocated against the separation of church and state—the law center has deep ties to NAR and is steeped in Washington’s extreme conservative religious right.
After our conversation, Don took us on a tour of his church. In the cozy, sunlit sanctuary, someone had left a flyer on a pew. The heading read, “Practical areas to prepare to speak out to societal issues.” The fourth item advised Christians, “People don’t care that you are a Christian, a citizen, or even a female…you are the enemy! Note: This would not happen to Muslims, Atheists, or BLM groups.” Lamb later told me that “You are the enemy of their agenda” would have been more accurate.
Branle, the Ephrata resident whose barn was vandalized, understands how it feels to be seen as the enemy. When she emailed local police about veiled threats she had received, an officer responded: “Can you elaborate on specifically what you perceive the threat to be? This appears to be a statement of opinion, which is protected speech.” After reporting a few more incidents to police, “I just stopped talking to them,” she said. “It felt a lot like it wasn’t helping.”
Groups affiliated with NAR are also the quiet heartbeat of institutions serving Lancaster’s neediest residents. TNT Youth Ministry, an evangelical group, provides classroom volunteers and field trip chaperones, and it runs Bible studies in local public schools. Another NAR-adjacent ministry, REAL Life Community Services, boasts that it is the “only full-time social services department” in one town.
Community service is a typical mission of faith groups the world over. But for Christians who believe they are called to influence the government, the objective is not spurred by faith alone. Rachel Tabachnick, an extremism researcher who studies NAR, notes that many of its adherents believe that “the way that you’re going to heal society is that you’re going to eliminate many government functions.” The church, not the government, will decide “whether to feed you or house you or clothe you.”
While in Lancaster, I visited the Blessings of Hope food distribution center, a Walmart-size grocery store that collects surplus food from manufacturers and makes it available to food pantries throughout the region at a deep discount. Rows of shelves filling the cavernous warehouse were crammed with giant bags of nacho cheese, dried chow mein noodles, gefilte fish, and onion ring mix. An army of volunteers, mostly women, many wearing the traditional haube hair covering for married Mennonite women, unloaded pallets of boxes.
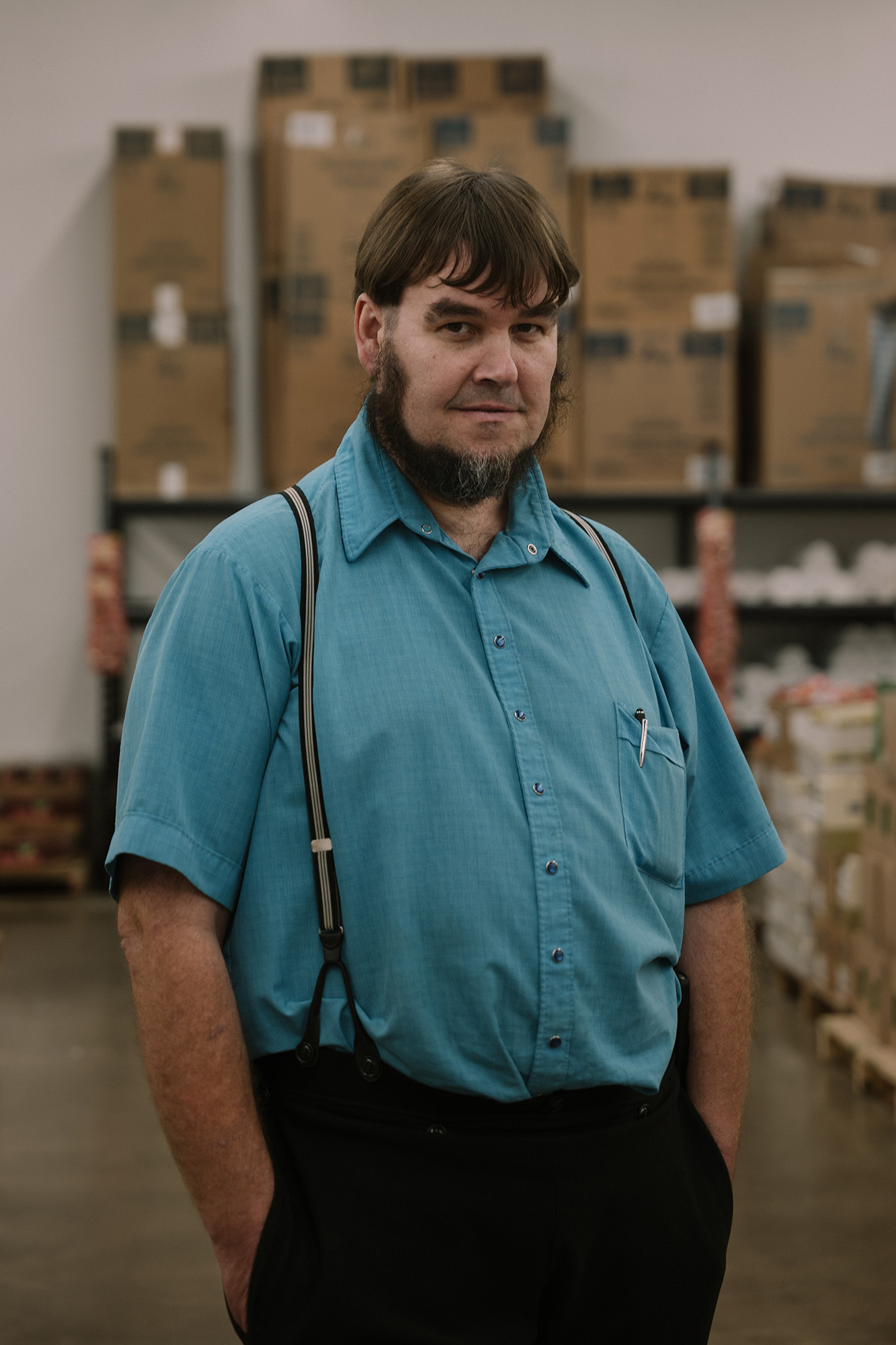


David Lapp, a 42-year-old father of 12 and CEO of Blessings of Hope, was in charge. He grew up Amish and speaks with the German-inflected lilt typical of the plain communities in the region. In the early 2000s, he and his eight brothers began to read more about evangelical Christianity. By 2006, after the Amish officially excommunicated them for straying from the church’s teachings, they began to follow NAR leaders, including prophet Andrew Wommack, who believes there is “a demonic deception that is blinding” those who spoke out against Trump. They have helped convert several Amish people, introducing them to Wommack’s work. Several of the Lapp brothers founded Blessings of Hope in 2006, and it has become a massive operation spread across five warehouses, providing 50,000 meals a day. Their work has drawn national attention: Ivanka Trump toured the distribution center during the 2020 campaign.
Lapp still dresses in the style of the Amish, with a handmade collared shirt, suspenders, and a bowl cut, because “we felt like God asked us to keep the traditional garb more as a bridge back to our people.” He sees his work as a divine calling. His organization’s closest competitor, he said, is the behemoth nonprofit Feeding America, which he described as “more of a government-run, government-funded organization” whose church participants “are not allowed to share the gospel when they’re giving out food.” Lapp, who believes in the Seven Mountain Mandate, sees publicly funded food pantries as a missed opportunity for the church. When government administers social services, he said, “they’re going to miss the hearts of the people.”


Back at Ephrata Community Church, I attended a Saturday evening service in the main building. Toddlers danced in the aisles as the worship band jammed. Some of the congregants had brought shofars in zippered carrying cases. After a somewhat banal sermon, I met executive pastor Jim Ehrman, who told me that he had only recently learned about NAR. Ephrata Community Church, he explained, had long had a “loose affiliation” with apostle Randy Clark, but “we don’t have a reference for it other than a group we care about was accused of being that.” I pressed further. Wasn’t his church about to host John Bevere, an NAR-affiliated pastor who has warned against the practice of tolerance?
“I had no idea he would have been associated with it,” Ehrman said. As far as the Seven Mountain teaching was concerned: “We do agree [the mountains] are there, but we’re very much like, ‘No, it’s who you are and how you carry yourself into those.’ There’s not some…mandate to take over.” When I told him about the prayer night, he seemed bemused. All the talk of spiritual warfare I had seen was “just the frame and the language they pick up,” he said.
Was Ehrman just being coy about his church’s connections to the New Apostolic Reformation, or was he genuinely naive to a movement that was so powerful and pervasive? In a sense, it didn’t matter. Another imperfect metaphor for the influence of NAR is climate change. Like it or not, it’s happening. The question for many pastors is how to steer their congregations through an increasingly chaotic and extreme religious landscape.
For Ehrman, the label was unimportant. What mattered was that armies of angels were indeed battling with the principalities of darkness. “There are literally unseen beings who are at odds with the work of God…on this earth,” he said. “And we believe that they are trying to influence things as well.”
Additional reporting by the Lancaster Examiner.







